
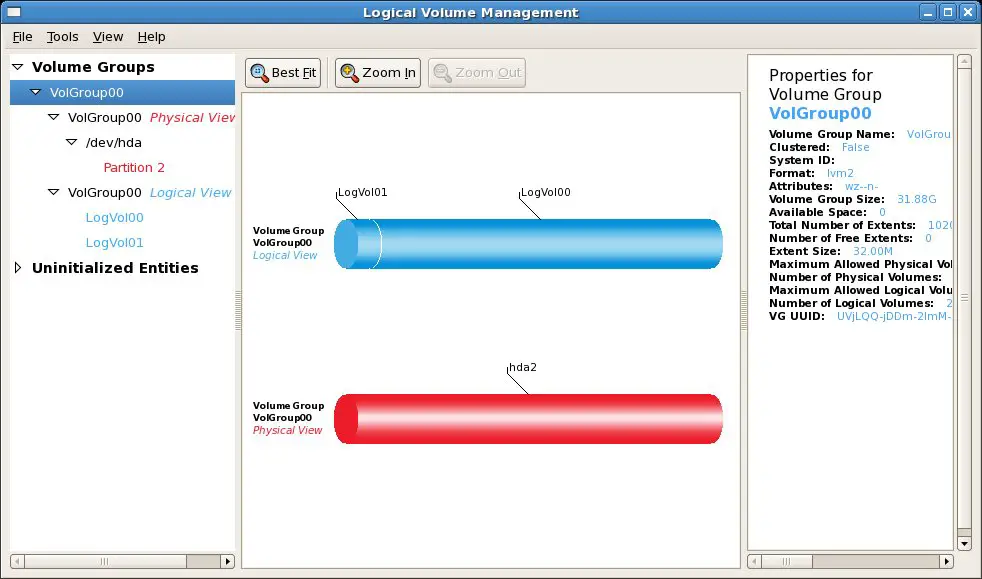
The boundaries of logical volumes can be defined independently of the boundaries of the host physical disk.Ī configuration in which one volume group contains multiple logical volumes is also supported.įor operation, please note the following:Ī logical volume for which a file system was constructed must be unmounted before backup or replication can be performed and remounted after the backup or replication has completed. The Logical Volume is a logical partition created from disk space assigned to the Volume Group. In traditional disk management your operating system looks for what disks are available (/dev/sda, /dev/sdb, etc.) and then looks at what partitions are available on those disks (/dev/sda1, /dev/sda2, etc.). Add the PV to the Volume Group (VG) and then extend the.

Next, create a new Physical Volume (PV) from that storage. With traditional storage, three 1 TB disks are handled individually. Storage space is managed by combining or pooling the capacity of the available drives. Compare LVM and standard partitioning in Linux. Logical Volume Manager (LVM) Traditional storage capacity is based on individual disk capacity.
#Logical volume manager how to#
LVM allows multiple logical volumes to be defined on a single physical disk (a logical volume is referred to as LU: Logical Unit). Logical Volume Manager allows for a layer of abstraction between your operating system and the disks/partitions it uses. The logical volume manager introduces extra layers of abstraction between the disks or storage devices presented to a. This article looks at how to extend storage in Linux using Logical Volume Manager (LVM).
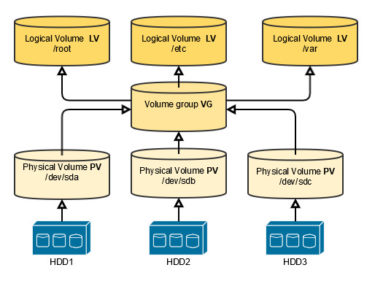
One volume group contains only one physical disk, and logical volumes are configured so that one physical disk includes logical volumes. LVM is a method of allocating hard drive space into logical volumes that can be easily resized instead of partitions. LVM volumes are volumes which are managed in units of volume groups containing logical volumes.ĪdvancedCopy Manager copies each physical disk that constitutes a volume group.Īn LVM volume that can be operated in units of logical volumes must satisfy the following conditions: On cloud servers, the Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is used to manage the storage space, and it puts a logical layer between the file system and the partitions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
